In recent developments within the financial markets, the United States Dollar experienced a notable decline, reaching its lowest point in two weeks on the Wednesday following a significant drop related to Tuesday’s events. This downturn in the dollar’s value against a diverse group of international currencies comes as market participants increasingly dismiss the possibility of the Federal Reserve maintaining current interest rates in their upcoming September meeting. Moreover, a recently reported moderate inflation rate has further fueled expectations among investors for potential interest rate reductions later within the year. This anticipatory sentiment has led to a widening gap in the yield spread observed between US bonds and those of other G10 nations. As such, upcoming US data releases, particularly those concerning inflation and consumer sentiment, are poised to be closely scrutinized for their potential impact on the dollar’s trajectory, especially in anticipation of the forthcoming Jackson Hole symposium.
Despite the calm inflation figures for the time being, the situation remains fluid and merits careful observation. The US Dollar Index commenced its decline in response to consumer inflation data released on a Tuesday, which aligned closely with market anticipations. Despite the looming presence of tariffs, their impact has, for the most part, been absorbed within corporate profit margins, sparing consumers from direct price increases. This dynamic offers the Federal Reserve some leeway to adjust its approach in response to softer employment data, potentially ushering in a series of interest rate reductions starting from September. This scenario, largely anticipated by markets, incorporates speculations of two additional rate cuts. Furthermore, public criticisms directed at Jerome Powell, the Federal Reserve Chair, by President Trump via social media have exerted additional downward pressure on the greenback, complicating forecasts for the US dollar.
A closer examination of inflation metrics revealed a modest monthly increase of 0.2% in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), with an annualized rise of 2.7%. Concurrently, the Core CPI, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, noted a 0.3% monthly uptick. Notably, energy sectors experienced a 1.1% decrease in prices, while food prices remained static. Even sectors highly susceptible to tariffs witnessed only marginal price increases, suggesting a trend where businesses are largely shouldering the tariff-induced costs. This absorption of tariffs by corporations hints at a complex interplay between trade policies and inflation dynamics.
The broader market consensus now leans towards the belief that, notwithstanding the immediate effects of higher tariffs, inflation is not expected to surge abruptly but might instead experience a temporary climb this autumn. Given the potential for a cooling economy and a softening job market, there’s a burgeoning expectation that CPI inflation could dip below the 2% target in the forthcoming year.
Looking ahead, the Federal Reserve’s impending decisions are eagerly awaited, especially with one more set of jobs and inflation reports due before the next meeting. Following a tepid jobs report and significant revisions to prior months’ data, along with the recent CPI figures aligning with predictions, the likelihood of the Federal Reserve initiating interest rate cuts as early as September has increased. This scenario could lead to a softer profile for the dollar towards the year’s end, conditional on the monetary policies adopted by other major central banks.
Attention within financial markets will also pivot towards the Producer Price Index (PPI) and the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index. The impending PPI report, due for release on a Thursday, holds particular importance as it precedes the PCE index—a favored gauge of inflation by the Federal Reserve. This index, notable for stripping out the volatile components of food and energy prices, serves as a crucial measure for assessing underlying inflation trends. The PPI data could offer valuable insights into potential shifts in inflationary pressures, especially in light of tariff impacts.
Furthermore, the health of consumer sentiment will be under scrutiny, with the upcoming release of retail sales data and the University of Michigan’s survey on inflation expectations providing a snapshot into consumer outlooks on inflation. Notably, the expectation for headline sales growth and core sales increment will offer key insights into consumer spending patterns, a critical component of economic health.
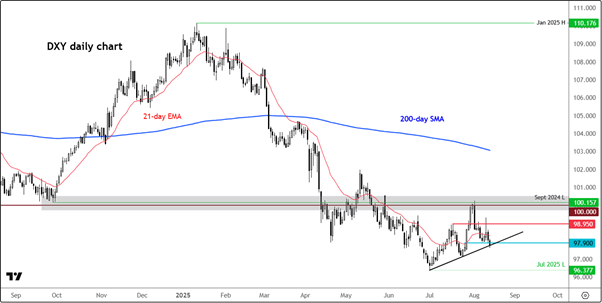
On the technical front, the US Dollar Index (DXY) displays potential for further movement, with support and resistance levels under close watch by traders. A breakdown below the current support trend might signal a test of previous lows, presenting a key juncture for the direction of the dollar in the short term.
In summary, the interplay between inflation data, consumer sentiment, and Federal Reserve policy decisions is poised to shape the trajectory of the US dollar in the coming months. As such, market participants and observers alike will be keenly watching the unfolding economic indicators and central bank communications for insights into the future movements of the greenback against a backdrop of global economic uncertainties.