In the rapidly advancing digital age we find ourselves in, the cybersecurity sector has been experiencing an unprecedented level of growth and transformation, primarily propelled by the advent of artificial intelligence (AI). The emergence of AI has significantly reshaped the cybersecurity landscape, amplifying not only the scope and scale of potential threats but also enhancing the sophistication of the defense mechanisms in place to counteract these threats. As AI-fueled attacks evolve to become more adaptive and increasingly difficult to discern, cybersecurity enterprises have risen to the challenge by developing AI-driven solutions designed to predict, thwart, and neutralize threats in a real-time environment. This constant technological tug-of-war has fostered an environment ripe for innovation and investment, positioning cybersecurity firms at the leading edge of one of the digital economy’s most critical sectors.
At the epicenter of this technological evolution is the critical role of data, an asset whose volume and strategic importance have surged exponentially. However, in this new AI-dominated era, it becomes clear that not all data is of equal value. The competitive advantage increasingly hinges on the quality of data rather than sheer quantity. The importance of acquiring rich, contextual, and accurately labeled datasets stands paramount, as it is essential for the training of effective AI models. These models are tasked with the delicate job of differentiating between benign and harmful behavior, marking a significant shift in the approach cybersecurity companies must take toward their data strategies. They now face the pressing need to invest significantly in enhancing the ways in which they collect, cleanse, and leverage data.
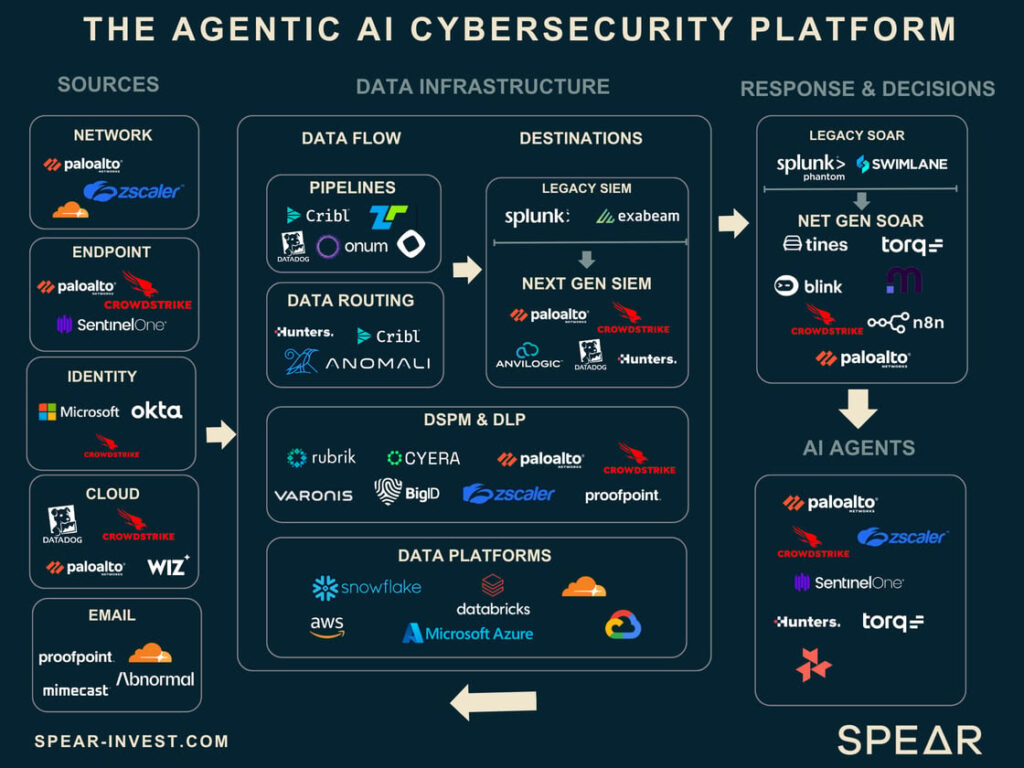
For the leading firms in the cybersecurity industry, establishing formidable data infrastructures has transitioned from a strategic choice to a fundamental necessity. As AI agents become increasingly integral to cybersecurity operations, companies are required to develop comprehensive pipelines, governance, and intelligence frameworks necessary to empower these agents. Entering the succeeding phase of cybersecurity, the victors will be those entities capable of evolving from mere data collection to orchestrating tangible outcomes and building unified platforms.
These underlying developments have significantly contributed to the maturation of the modern Security Operations Center (SOC), now augmented by AI. Although the ultimate aim lies in the integration of AI Agents, the underlying value is profoundly rooted in both the Data Source and the Data Infrastructure Layer.
The Modern SOC: The Evolution of Cyber Defense’s Central Hub
The SOC stands as the central nerve of cybersecurity operations, acting as the conduit through which every alert or response, from endpoint to cloud, is processed. Although SOCs have been a part of the cybersecurity framework for decades, their role and functionality have undergone significant enhancements in recent times.
The contemporary SOC transcends the traditional model of a dashboard displaying static data. It embodies a sophisticated system where data from varied sources, including networks, endpoints, identities, and the cloud, is integrated into actionable insights. The foremost challenge for a SOC lies in its ability to process and filter through this incoming data, which is often improperly labeled and formatted diversely.
From the perspective of public company investment, there’s a keen focus on identifying how each company is positioned to capture a substantial share of this evolving marketplace. As highlighted by Palo Alto management, the demand from customers for seamless integration underscores the imperative that companies delivering cohesive platforms are poised for success.
Leaders in various domains of cybersecurity, such as network, endpoint, identity, cloud, and email security, are in possession of vast data reserves. This positions these companies uniquely to capitalize on the value ingrained within this data.
Strategic Data Leverage by Cybersecurity Titans
For instance, CrowdStrike Holdings Inc, renowned for its prowess in Endpoint Security, manages over 5 trillion events weekly, makes more than 150 million indicator of attack (IOA) decisions every second, hosts upwards of 15 petabytes of data in the cloud, and secures over 1 billion containers on a daily basis. Similarly, Zscaler, a titan in Network Security, processed over 100 trillion transactions, blocked more than 60 billion threats, and enforced over 5 trillion policies in a single year.
The distinction for these companies in the forthcoming growth phase will, unsurprisingly, hinge on how they filter, organize, and utilize their data. It is no surprise then that most significant bolt-on acquisitions have targeted the Data Infrastructure layer, building upon the solid foundations each company has established in their respective core markets.
For example, Crowdstrike’s acquisition of Flow Security, a specialist in cloud data runtime security, to bolster its DSPM offerings for approximately $110 million in March 2024 underscored this trend. Similarly, Palo Alto Networks’ acquisition spree, including Dig Security for Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) for $200–$400 million in October 2023, IBM’s QRadar to add SIEM capabilities for $1.14 billion in September 2024, and Protect AI for approximately $600–$700 million expected to close in Q1 2026, underlines the strategic importance of augmenting data infrastructure. Zscaler’s acquisition of Avalor, a data fabric platform, for $350 million in March 2024, followed by the announcement of acquiring RedCanary, a Managed Detection and Response (MDR) platform, for $675 million, expected to close in August 2025, further solidifies this strategic direction.
These strategic acquisitions and investments showcase the cybersecurity industry’s shift towards leveraging data more effectively as part of a broader strategy to enhance security measures in the face of evolving threats. The integration of AI and sophisticated data infrastructure is setting new standards in cybersecurity, ensuring firms are better equipped to protect against and respond to cyber threats in an increasingly digitalized world.